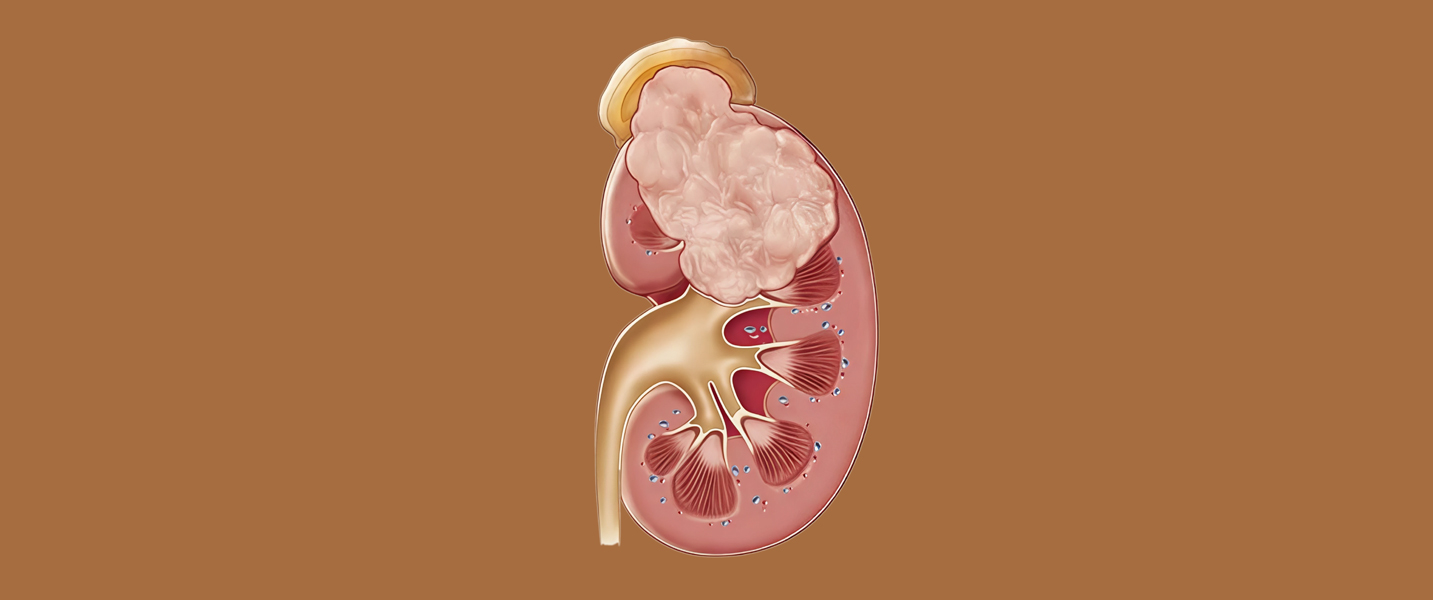
What is Renal cell carcinoma (RCC)?
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the most common type of kidney cancer, accounting for about 90% of cases. It originates in the lining of the proximal convoluted tubule, a part of the small tubes in the kidney that transport waste molecules from the blood to the urine.